Written by Louis Nottingham and Betsy Beers, WSU TFREC Entomology. Updated February 2020.
Background

Pear psylla control is becoming increasingly difficult, especially in regions of the Pacific Northwest like the Wenatchee Valley where pear orchards dominate the landscape. In high-pressure locations, an important factor in pear psylla control is delaying their immigration and egg laying in the early spring. A method that is gaining popularity is early season repellency, as is seen in the increased use of the kaolin clay product Surround WP. Repelling overwintered adults during the early season delays egg laying until later in the spring, which causes psylla generations to occur in clear increments, and thus allowing for more precise insecticidal control. Additionally, trying to control overwintering adults with insecticides is often a fruitless effort (no pun intended), because of their high mobility among orchards and uncultivated areas, as well as their increasing resistance to most insecticides. Due to the success of Surround WP as a repellent, we sought to determine if other agricultural and non-agricultural products may also act as repellents for overwintering psylla. Products were chosen based on stated interest from field advisors, growers or researchers. Table 1 has each product listed and the reason it was chosen.
Methods
Individual pear trees (potted d’Anjou, two years old, bud-break stage) were sprayed with materials and placed into a large cage in the greenhouse (Figure 1). Overwintering psylla were collected from an untreated pear Orchard in Wenatchee in March of 2017, and released into the cage. After a week, adults and eggs were counted on each pear tree. Two identical experiments were conducted; each containing 3 replicates of treatments.
Results
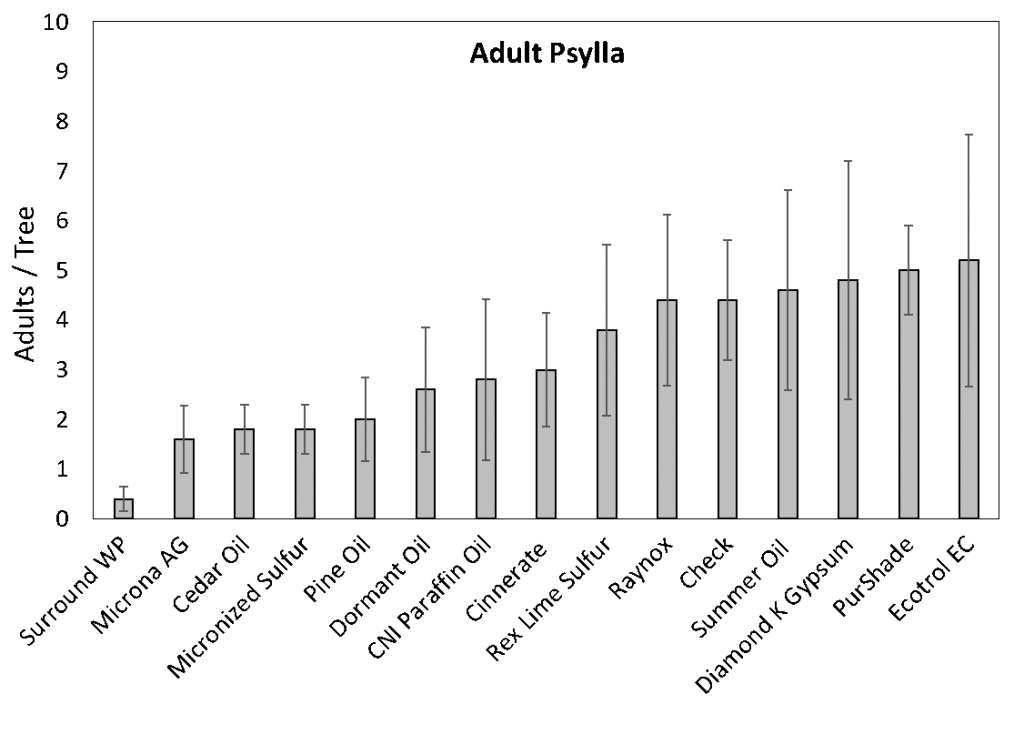
The results of this experiment were not astounding from a statistical standpoint; however, the general trends will help narrow down which materials are worth pursuing in future experiments and field trials. Overall, Surround appeared to be the most effective at repelling psylla, having the lowest numbers of adults (Figure 2) and eggs (Figure 3). Cedar oil, pine oil, and Microna AG also seem to be in the upper bracket of repellency. CNI paraffin oil, dormant oil, and Cinnerate showed marginal levels of repellency; while the rest did not appear to have a detectable effect. Additionally, no materials resulted in visibly detectable phytotoxicity.
Conclusions
Surround WP appears to be the best product for repelling adult psylla, of those we tested. There is certainly potential for other products such as the Surround-like products (Microna appears especially promising based on these results) and conifer oils. Surround-type products should be of particular interest for a few reasons. Surround WP is becoming more expensive with greater use, and seasonal demand often outweighs the supply. Although similar products were not as effective in this trial, field results may differ. Also, formulations may improve in the future to increase efficacy; remember, the formulation for Surround has changed and improved since initial release. Conifer oils (pine and cedar) are probably too expensive to justify largescale use, currently. However, these products are not manufactured for agricultural use, which could change if the use of conifer oils appears to be a method worth pursuing. It is reasonable to think that an agricultural-use product could be developed at a reasonable price if the demand is present.
Table 1. Product list and reason for selection in trial
| Trt. | Product | AI in product: product/200 ml | Expected type of repellent – reason for selection |
| 1 | IAP 440 (summer) | 98.5% mineral oil: 8 ml | Tactile repellent. Commonly mixed with insecticides. |
| 2 | IAP 470 (dormant) | 98.5% mineral oil: 8 ml | Tactile repellent. Commonly mixed with insecticides. |
| 3 | CNI Paraffin Oil 2 | Mineral oil: 2-ml | Tactile repellent. Commonly mixed with insecticides. |
| 4 | Rex Lime Sulfur | 28% calcium polysulfide: 14 ml | Olfactory repellent. Strong smell of sulfur which is toxic to many arthropods. |
| 5 | Cedar Oil 1,2 | 100% cedar essential oil (Jedwards Inc.): 4 ml | Olfactory repellent. Psylla thought to migrate away from conifers (overwintering sites) in early spring. |
| 6 | Pine Oil 1,2 | 100% pine essential oil (Jedwards Inc.): 4 ml | Olfactory repellent. Psylla thought to migrate away from conifers (overwintering sites) in early spring. |
| 7 | Cinnerate | 60% cinnamon oil: 4 ml | Olfactory or tactile. Strong smell and known toxin to mites and soft-bodies insects. |
| 8 | Ecotrol EC | 10% rosemary oil and 2% peppermint oil: 1 ml | Olfactory repellent. Strong smell and occasional use as insecticide |
| 9 | Raynox 2 | carnauba wax and modified clay: 12 ml | Tactile repellent or visual masking. Similar to Surround. Liquid formulation of clay product |
| 10 | PurShade 2 | 62.5% calcium carbonate: 5 ml | Tactile repellent or visual masking. Used for protection against fruit sunburn. |
| 11 | Surround WP | 95% kaolin clay: 20 g | Tactile repellent or visual masking. Unpleasant powdery/dry surface. Odd color prevents host detection. |
| 12 | Diamond K Gypsum 1,2 | 52% potash (K2O) and 18% sulfate (SO4): 20 g | Tactile repellent or visual masking. Similar to Surround. |
| 13 | Microna AG 2 | 95% calcium carbonate: 20 g | Tactile repellent or visual masking. Similar to Surround. |
| 14 | Microthiol Disperss Wettable Sulfur | 80% sulfur: 13.6 g | Olfactory repellent. Strong smell of sulfur which is toxic to many arthropods. |
| 15 | Check | H20 | – |
1Use as a foliar application in pears is not stated on label and is not exempt from FIFRA under the Minimum Risk Exemption regulations in 40 CFR 152.25(f).
2 Pear psylla is not listed on label as a target control organism.

Additional Information
Pear IPM Project
WSU Research and Extension Betsy Beers, Louis Nottingham, Tianna DuPont and Christopher Strohm in collaboration with many consultants in the area launched a renewed effort in pear IPM in the spring of 2017. This project includes new research trials and extension efforts to find solutions to pear pest management challenges. Keep tuned to the news section of treefruit.wsu.edu for updates (subscribe here). A summary of Pear IPM information will be available at https://treefruit.wsu.edu/crop-protection/pear-ipm/.
Contacts
 Louis Nottingham, PhD
Louis Nottingham, PhD
Research Professor
Washington State University
Tree Fruit Research & Extension Center
1100 N Western Ave., Wenatchee, WA 98801
email: louis.nottingham@wsu.edu
Disclaimer
Some of the pesticides discussed in this presentation were tested under an experimental use permit granted by WSDA. Application of a pesticide to a crop or site that is not on the label is a violation of pesticide law and may subject the applicator to civil penalties up to $7,500. In addition, such an application may also result in illegal residues that could subject the crop to seizure or embargo action by WSDA and/or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. It is your responsibility to check the label before using the product to ensure lawful use and obtain all necessary permits in advance.
Use pesticides with care. Apply them only to sites listed on the labels. When mixing and applying pesticides, follow all label precautions to protect yourself and others around you. It is a violation of the law to disregard label directions. If pesticides are spilled on skin or clothing, remove clothing and wash skin thoroughly. Store pesticides in their original containers and keep them out of the reach of children, pets, and livestock. The information in this correspondence is not meant to endorse the use of any product.
