Printable Handout – Station 3 Discovering New Codling Moth Entomopathogenic Fungi
Problem
Effective codling moth management requires a diversity of active ingredients and modes of action. Organic management is limited to only a handful of options, and they need more to prevent resistance development.
Project Goal
Discover, characterize, and develop new codling moth entomopathogenic fungi.
Background
- 14,000 Codling moth larvae were collected in cardboard bands in 2023
- 8 were screened for entomopathogenic fungi
- 3 were found infected
- Beauveria bassiana
- Metarhizium robertsii
- Ophiocordyceps sp.
- B. bassiana and M. robertsii show the most promise in initial assays
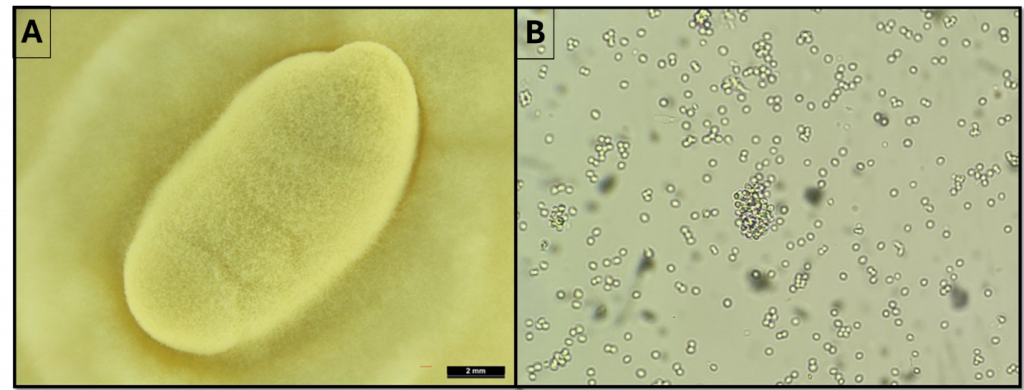
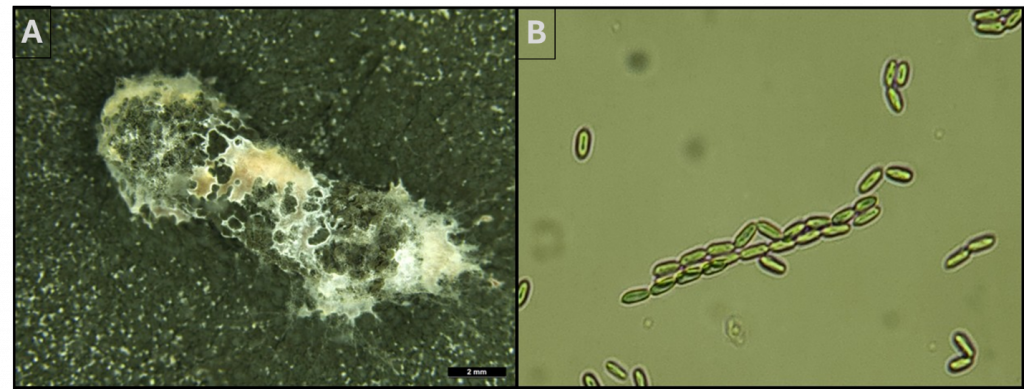
Future
- Continue infecting healthy codling moth larvae
- Select for the most virulent strains
- Develop those strains into biopesticides
- Identify, screen, and develop new strains from new collections
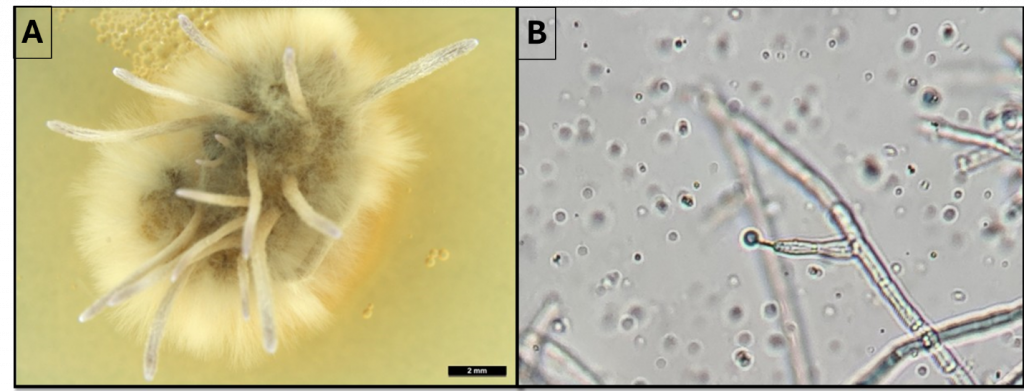
Thank you to funders
USDA
Washington Tree Fruit Research Commission
WSU Center for Sustaining Agriculture and Natural Resources
Contacts
RT Curtiss
rcurtiss@wsu.edu
Cesar Reyes Corral
cesar.reyescorral@wsu.edu
Tobin Northfield
tnorthfield@wsu.edu
